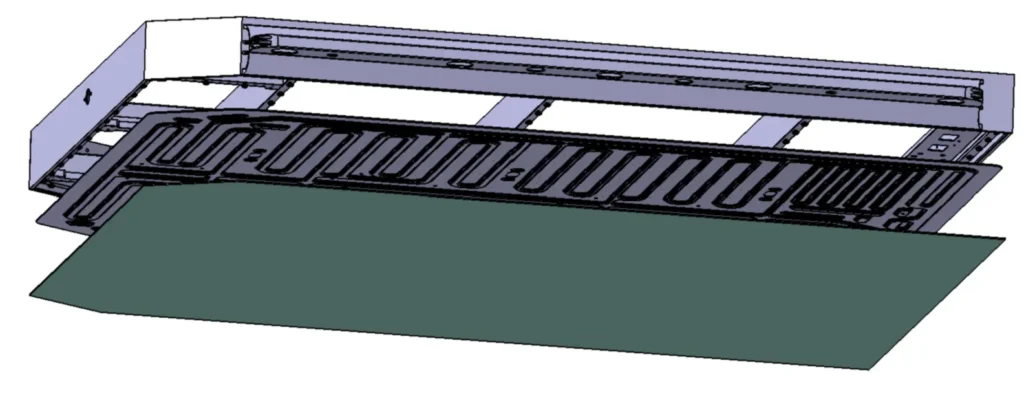
To improve battery heat transfer performance, the current mainstream battery liquid cold plate utilizes bottom-mounted liquid cooling, using stamped liquid cooling plates. The main types of liquid cooling plates used on the battery market include stamped liquid cooling plates, microchannel cold plate, and extruded aluminum liquid cooling plates. I will describe stamped liquid cooling plates in the function of structure, materials, and pack arrangement.
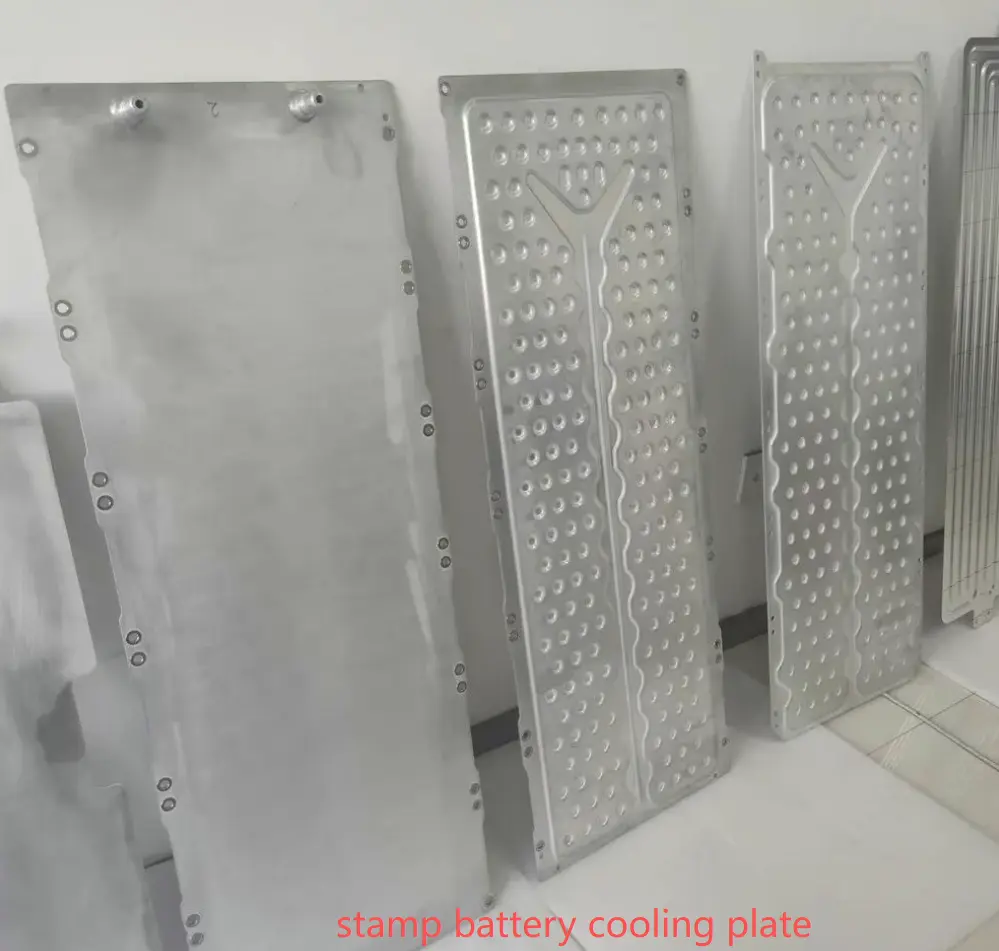

1.Advantages of stamped liquid cold plates
The stamped liquid cold plate is usually installed at the bottom of the battery pack and contacts the battery cell through thermal paste. Its main advantage is its large heat dissipation area, especially in terms of thermal management.
Secondly, stamped liquid cooling plates can be directly integrated on top of the battery cell, replacing the top cover with a liquid cooling plate, which also saves component costs. For example, the cold plate of BYD Seal replaces the top cover.
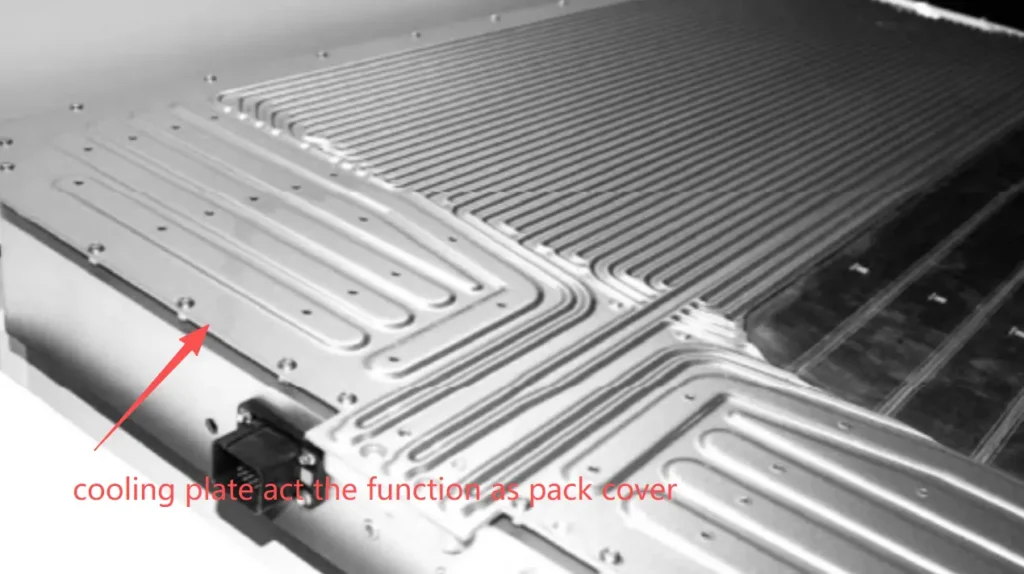

Lastly, the flow channel pattern design of the stamped liquid cooling plate is very free. The flow channel direction&shape can be designed according to the battery cell arrangement to minimize flow resistance and improve temperature uniformity.
2. Exploded diagram of stamped liquid cooling plate
The stamped liquid cooling plate structure consists of a channel plate, a base plate and a nozzle, which are brazed into one piece.
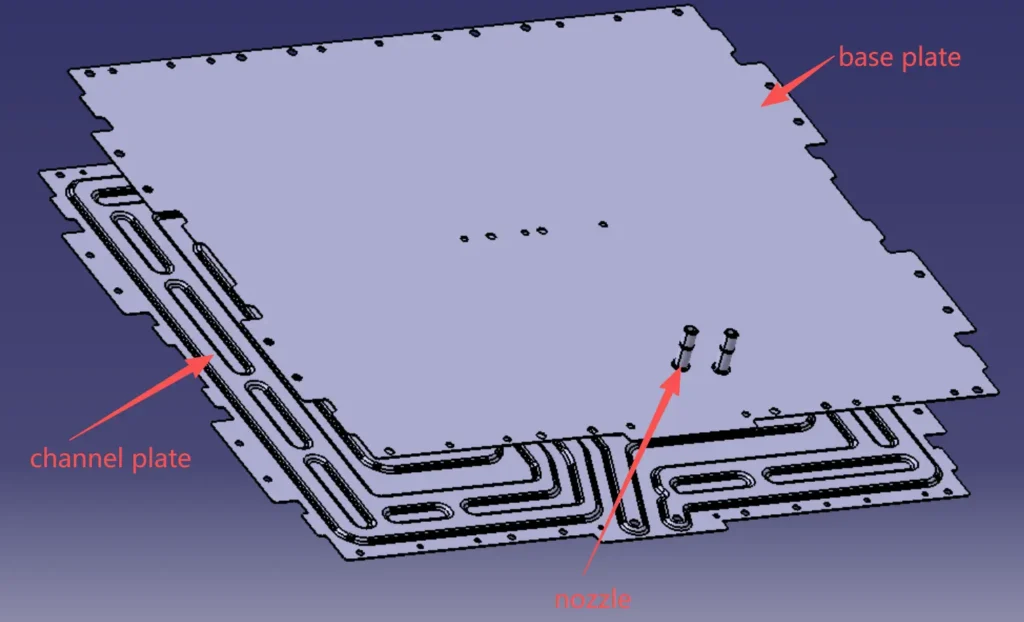
3.Channel plate
The channel plate, also known as the lower plate, is formed using a single-step drawing and stamping process, resulting in high production efficiency and a high product yield rate. The channel stamping depth of a liquid cooling plate is typically designed between 3 and 5 mm to balance flow resistance and heat transfer efficiency. The current mainstream design thickness for channel plates is 1 mm, emphasizing lightweight design, high versatility of material, and sufficient raw materials.
4.Base plate
The base plate, also known as the upper plate or flat plate, generally has no channel features and serves as the contact for the battery cells. Base plates are typically formed by stamping, but small batches can be directly laser-cut without the additional mold-making costs. Base plate thickness is generally between 1.2 and 2 mm to achieve good flatness after brazing.
5. Material comparison between base plate and channel plate
For furnace brazing, the materials used for the base plate and runner plate are different. The following are the materials used by our regular customers.Validated OK by our battery cooler DV and PV test.
| Component | Aluminum material | Surface treatment |
| base plate | 3003MOD | Epoxy resin powder coating,optional,better for anti-corrosion |
| Channel plate | 3003MOD+10%4045/4343 | Epoxy resin powder coating,optional,better for anti-corrosion |
| nozzle | 3003 | NA |
6. Battery pack lower casting arrangement
The stamped liquid cooling plate is usually integrated into the bottom of the battery lower box and connected via FSW or FDS. The bottom is protected by a bottom guard plate.