What is the purpose of PV testing? What tests are required for battery liquid cooling plates? What are the test methods and verification standards for each test item? Based on 14 years of design experience, communication with various customers, and field testing, David has compiled the following PV test list.See below step by step the pv testing definition.
1.The difference between PV and DV testing
Battery cooling plate belongs to dv pv testing automotive, and is an automotive part.PV and DV testing are different, and the sample status and verification purposes are also different.
- DV prototypes are typically produced using soft tool and are handmade prototypes, often produced on non-mass production lines. DV testing primarily verifies functional and performance requirements. Once DV verification passes, the design can be frozen and the production molds and production lines can be officially launched.
- PV sample are produced on mass production lines using production tool, meeting both mass production quality requirements and production cycle requirements. After passing PV testing, they can enter the PPAP stage. Audit teams from customer quality,R&D and buyer will audit the production line in site, when audit result is OK, the PPAP small-batch production can begin.
2.Full dimension and appearance PV test items
The PV test items of the battery liquid cooling plate, full dimension check and appearance are routine items. Generally, after the PV on site audit, the appearance limit sample will be signed with the customer and stored.
Table 1 Full dimension and appearance PV test items
| Nb.# | Test items | Experimental methods | Evaluation Criteria | Number of samples |
| 1 | Cold plate appearance and weight | Appearance Inspection EnvironmentVisual Inspection Distance: 500mm between the human eye and the surface of the object being inspected;Visual Inspection Time: No more than 30 seconds per area (defects not visible within 30 seconds are not counted); Visual Inspection Conditions: Conducted under simulated end-use conditions, without the use of a magnifying glass; Inspection Angle: ±45° from vertical;Lighting Conditions: Natural light or near-natural light (e.g., 40W fluorescent light at a distance of 500mm); Visual Acuity: Minimum 1.0, with normal vision; no color blindness, strabismus, or astigmatism; Inspection Order: Exterior surface first, then interior surface. | The liquid cooling plate must be clean and have a smooth surface. No sharp scratches, cracks, weld defects, burrs, or other defects are allowed. No visible lateral or longitudinal deformation is allowed. The weight must meet the requirements. | 3 |
| 2 | Full dimension measurement | Use calipers and three-dimensional coordinate measuring machines to measure the dimensions required in the 2D drawings | Meet the drawing requirements | 3 |
3.Airtightness and pressure drop PV test items
Pressure loss is a key consideration during liquid cold plate design, as it aims to reduce system energy consumption . Therefore, PV testing requires coolant pressure drop testing, and different pressure drop are tested at different flow rates. For more information on comparing simulated with actual measurements, please read our this post. Cold plate airtightness is also crucial; poor airtightness can lead to liquid leakage.
Table2 Airtightness and pressure drop PV test items
| Nb.# | Test items | Experimental methods | Evaluation Criteria | Number of samples |
| 1 | Coolant pressure drop test | Water resistance (assembly including rubber hose, flange, and cold plate core) at room temperature and water flow rates of 5, 10, and 15 L/min | Meet customer target pressure loss criteria per different flow rate | 3 |
| 2 | Water cooling plate airtightness test | The product is tested on a helium test equipment stand. One end of the inlet is connected to the helium test equipment, and the other end of the outlet is connected to the plug. The equipment sealing cover is closed and the test is started. The leakage rate is tested using a 0.25MPa pressure test.(some customer may define 0.2,0.3,or 0.15Mpa,it depend) | Leak rate meet customer requirement | 3 |
4.PV durability test
Liquid cooling plates require long-term operation and require environmental and strength durability testing. The following table shows the PV test items for liquid cooling plate durability testing.
Table 3 PV durability test items
| Nb.# | Test items | Experimental methods | Evaluation Criteria | Number of samples |
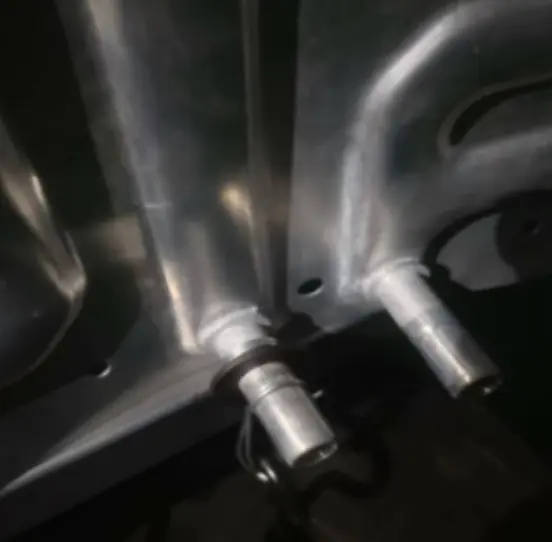
| 1 | Water nozzle braze joint strength test | Apply a force of 500N in the radial direction of the joint, maintain the tension for 1 minute, and observe whether there is any tearing or loosening at the joint weld. | There are no cracks or looseness in the welds after the test | 3 |
| 2 | Burst test for battery cooling plate | Water or coolant is introduced into the cooling plate core.Pressure: Increase pressure at a rate of 0.5 bar/sec to 4.0 (positive pressure resistance) bar (no leakage). Continue increasing pressure at a rate of 0.5 bar/sec until failure occurs. Record the failure pressure and location. | Burst pressure not less than 10 bar | 3 |
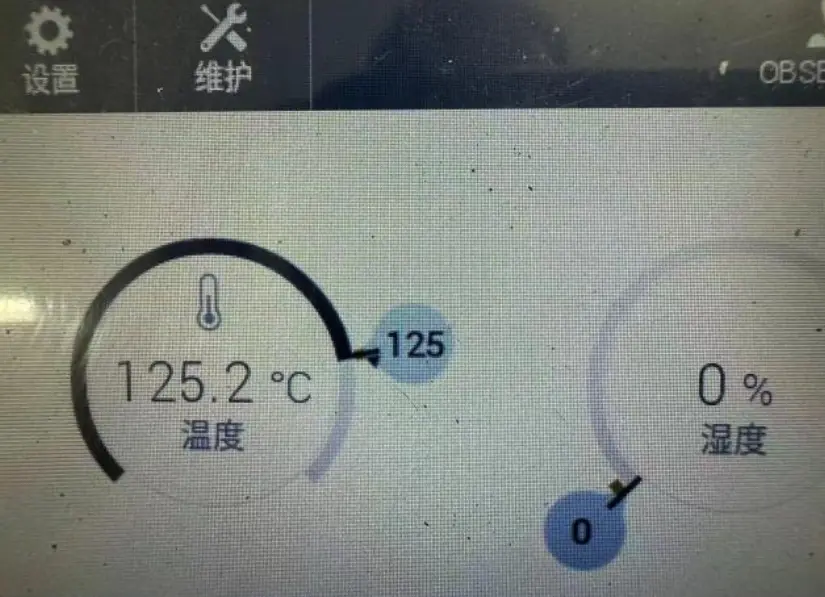
| 3 | High temperature resistance for battery cooling plate | After the liquid cooling system components are assembled, place them in a 125°C environmental chamber and introduce 50% ethylene glycol and 50% water (volume ratio) into the system at a flow rate of 10L/min and a temperature of 125°C ± 2°C for 200 hours. After the test, return to normal temperature for airtightness test. | No leakage and no crack after test. | 1 |
| 4 | Low temperature resistance for battery cooling plate | After the liquid cooling system is assembled, it is placed in a -40°C environmental chamber. 70% ethylene glycol and 30% water (volume ratio) are introduced into the system at a flow rate of 10L/min. The product is then placed in a high and low temperature chamber and tested for 200 hours. After the test, the system is returned to normal temperature for airtightness testing. | No leakage and no crack after test. | 1 |
| 5 | Temperature shock test for battery cooling plate | Test medium: 50% ethylene glycol + 50% aqueous solutionMedium temperature consistent with ambient temperatureNumber of cycles: 10The sample was placed horizontally in the test chamber. The chamber temperature was cycled between -35°C and 55°C. The medium pressure was at least 150 kPa (for passenger cars). The test was conducted in a temperature cycle from -35°C (low temperature) to 55°C (high temperature) to -35°C (low temperature). Temperature accuracy was controlled within ±3°C, with a high/low temperature switching rate of ≥3°C/minute. The holding time in the high and low temperature zones was 30 minutes each. | No leakage and no crack after test. | 1 |
| 6 | Pressure alternating test | Conducted on a high-temperature pulse test bench:Test medium: 50% ethylene glycol + 50% aqueous solutionTest temperature: 110±5°CPressure cycle time: 6s-10s, including a hold time of 3s-5s;Pressure alternating range: 30-125-30 kPaNumber of tests: 20 x 10^4 (leakage checked every 50,000 cycles) | No leakage and no crack after test. | 1 |

5.PV corrosion testing
The corrosion test of the liquid cold plate includes external corrosion and internal corrosion, which are listed below.
Table 4 PV corrosion testing items
| Nb.# | Test items | Experimental methods | Evaluation Criteria | Number of samples |
| 1 | External Salt spray corrosion test | External corrosion test need to carry out per customer requirement,different PH and lead time | Meet airtightness test | 1 |
| 2 | Internal corrosion test | Mixed solution temperature: 90±2°CMixed solution flow rate: 0.3 L/sOperate at the required flow rate for 76 hours, with each cycle consisting of an 8-hour shutdown. During this downtime, check the pH and refill the solution, for a total of 14 cycles. The solution is inspected for both pH and appearance. During the test, no pH fluctuation exceeding ±1°C is permitted, and no turbidity or precipitation is permitted.The mixed solution consists of 40% antifreeze and 60% ASTM antifreeze (volume ratio).Antifreeze type: 45% ethylene glycol antifreeze, freezing temperature: -30°C. ATM solution: Prepare 1 L of distilled water with 148 mg of sodium sulfate, 165 mg of sodium chloride, and 138 mg of sodium bicarbonate.During the test, no pH fluctuation exceeding ±1°C is permitted, and no turbidity or precipitation is permitted. | Meet airtightness test | 1 |
6.Is it necessary to complete PV testing before mass production?
Yes, PV testing is a key step in verifying the reliability and quality of battery liquid cooling plates. Passing all PV tests is a prerequisite for mass production. How long does the test take? Taking the pressure drop test as an example, please refer to our blog post on pressure drop test time. Is it expensive? We’ll also write a post for a pressure drop test cost as an example to illustrate the cost of testing.
In fact, in order to reduce the cost of PV testing, some tests can use the previous test reports and do not need to be redone. In our company, we also have a test bench and can perform some PV testing projects for customers free of charge.That’s say,some pv test reports can be carryover.
7.How to ensure the success rate of PV testing
PV testing has many requirements and is therefore expensive. Failure not only wastes money but also impacts project timelines. To ensure a successful PV test, design engineers must possess strong design capabilities and extensive project experience. At Vehicle Thermal, for example, we have numerous production projects, extensive experience communicating with numerous clients, and a deep understanding of their testing requirements.
At the same time, simulation is needed in the early stages to identify the risk of PV failure in advance, such as performing pressure drop simulation analysis.
In the realm of product development and manufacturing, partnering with a seasoned supplier is crucial. A top-tier supplier should possess a robust Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for both Design Verification (DV) and Production Verification (PV) testing.
Moreover, state-of-the-art facilities are essential for conducting these tests accurately and efficiently. At VEHICLETHERMAL, we go beyond just having the latest equipment. Our comprehensive SOP for DV and PV testing is meticulously designed to cover every aspect of product development.
We offer a full suite of end-to-end services, starting from expert design assistance to seamless mass production. Our extensive experience in international OEM projects has equipped us more know in battery cooling cases.
8.Keys take away
If you are our client, you can ask our R&D manager David to provide you the pv test full form.